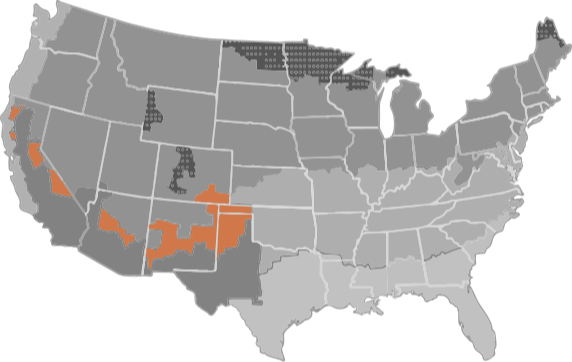
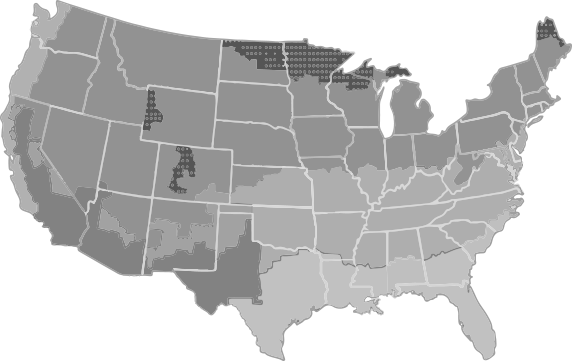
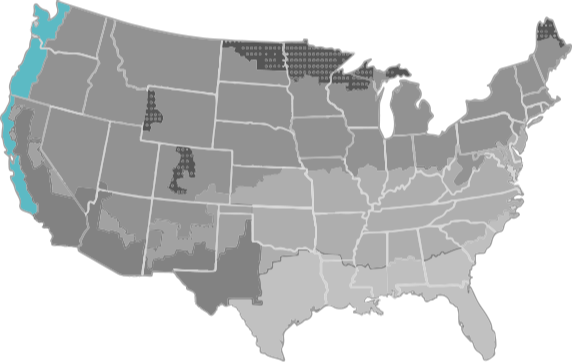
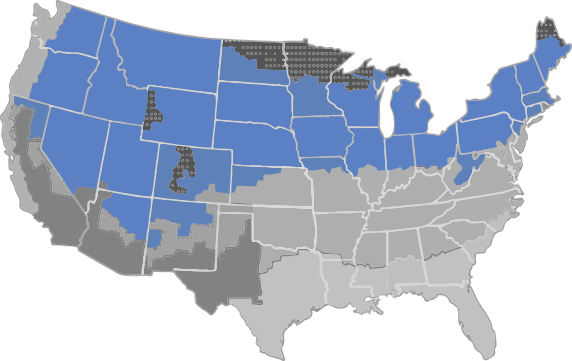
There are eight climate regions in North America, seven in the continental United States.
What defines each climate zone can be a bit technical, but understanding it can supply a potential buyer or builder with very useful information.
|
MARINE
|
COLD
|
VERY-COLD
|
MIXED-HUMID
|
|
HOT-HUMID
|
HOT-DRY
|
MIXED-DRY
|
SUBARCTIC
|
- MARINE
- COLD
- VERY-COLD
- MIXED-HUMID
- HOT-HUMID
- HOT-DRY
- MIXED-DRY
Some terms to know:
You might be encountering some of these terms for the first time.
Heating degree days
Heating degree days refers to an annual accumulation of heating demand.
Assuming a baseline temperature of 65°F, any climate zone will have a heat load based on the amount of days it is above or below that point. If, for example, the temperature remains at 50°F for a 24-hour period, that would equate to 15 heating degree days
Wet bulb temperature
This is a way to measure heat and humidity. The wet bulb temperature is the lowest temperature to which air can be cooled by the evaporation of water into the air. Because higher humidity means it takes longer for a home (and the people in it) to cool down, the higher the wet bulb temperature is, the harder it is for sweat to evaporate, and for bodies to cool down.
A marine climate is defined as a region that meets all of the following criteria:
- A coldest month average temperature between 27°F and 65°F.
- A warmest month average of less than 72°F.
- At least 4 months with average temperatures higher than 50°F.
- A dry season in summer. The month with the heaviest precipitation in the cold season has at least three times as much precipitation as the month with the least precipitation in the rest of the year.
A cold climate is defined as a region with between 5,400 and 9,000 heating degree days.
A very cold climate is defined as a region with between 9,000 and 12,600 heating degree days.
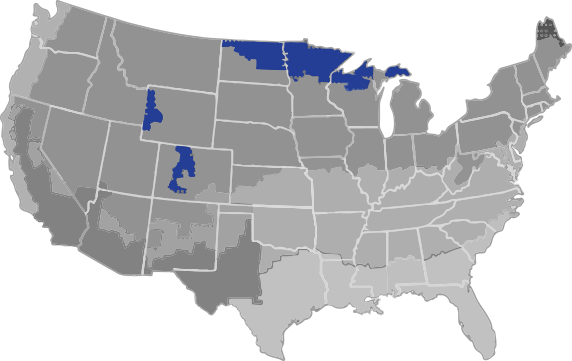
A mixed-humid climate is defined as a region that receives more than 20 inches of annual precipitation, has approximately 5,400 heating degree days or fewer, and where the average monthly outdoor temperature drops below 45°F during the winter months.
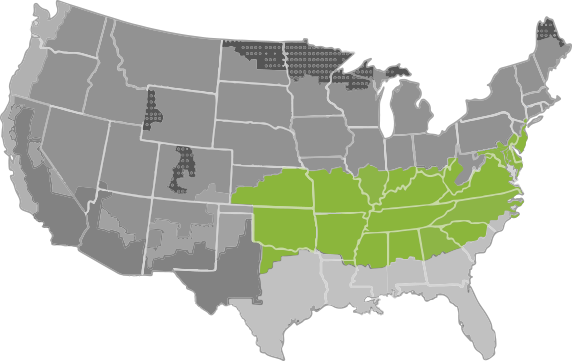
A hot-humid climate is defined as a region that receives more than 20 inches of annual precipitation and where one or both of the following occur:
- A 67°F or higher wet bulb temperature for 3,000 or more hours during the warmest six consecutive months of the year; or
- A 73°F or higher wet bulb temperature for 1,500 or more hours during the warmest six consecutive months of the year.
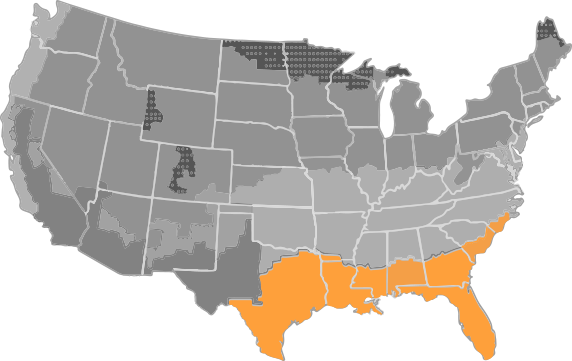
A hot-dry climate is defined as a region that receives less than 20 inches of annual precipitation and where the monthly average outdoor temperature remains above 45°F throughout the year.
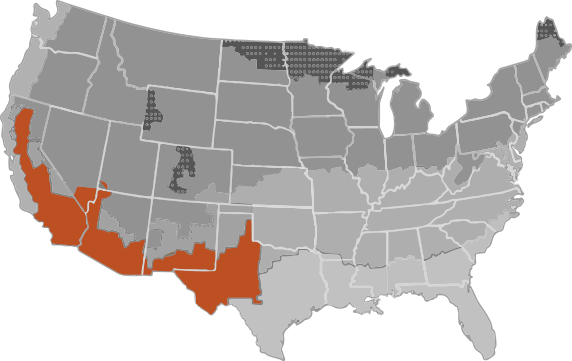
A mixed-dry climate is defined as a region that receives less than 20 inches of annual precipitation, has approximately 5,400 heating degree days or less, and where the average monthly outdoor temperature drops below 45°F during the winter months.